The world of textiles is vibrant and varied, with color playing a crucial role in design and market appeal. Basic dyes, a significant category within the dyeing industry, offer a unique blend of bright hues and easy application, making them highly favored for various textile materials. According to Dr. Emily Hart, a noted expert in textile chemistry, “Basic dyes serve as the foundational coloring agents in the fabric industry, providing an array of colors that enhance both aesthetic and practical aspects of textiles.”
These dyes are primarily cationic, meaning they carry a positive charge, which allows them to adhere effectively to negatively charged fibers. As a result, basic dyes are widely used in dyeing acrylic, nylon, and some polyester fabrics. Their versatility extends to applications in fashion, home textiles, and technical textiles, underscoring their importance in modern textile production.
Understanding the properties, applications, and significance of basic dyes not only informs manufacturers and designers but also educates consumers about the choices available in the textile market. With this foundational knowledge, stakeholders can make informed decisions regarding dye selection and its impact on the overall textile performance and visual appeal.
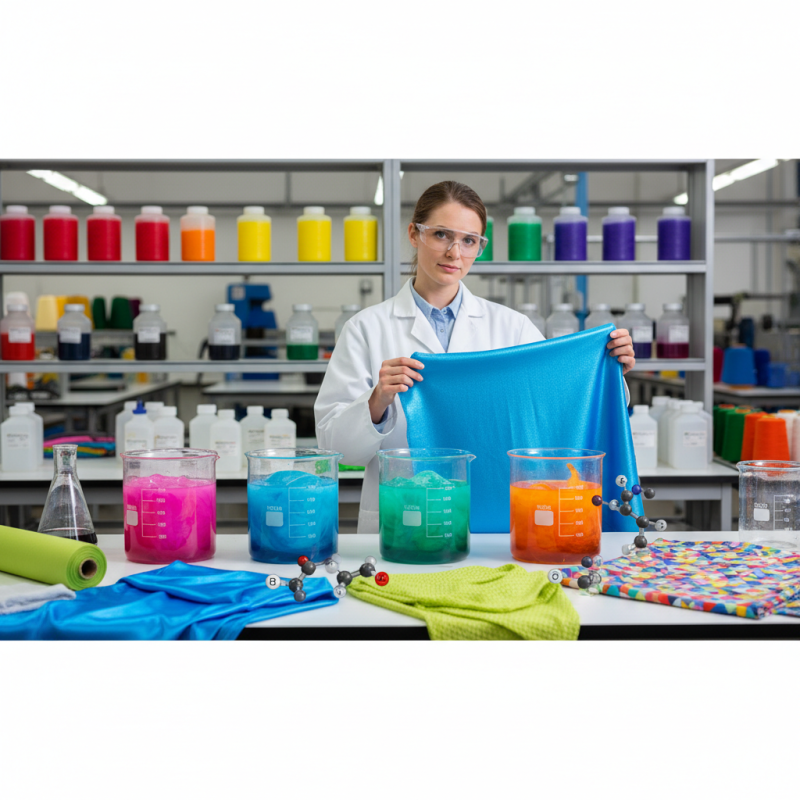

Basic dyes are a category of synthetic dyes that hold significant importance in the textile industry due to their vibrant colors and ease of application. These dyes, typically cationic in nature, are used primarily on acrylic fibers, some synthetics, and in applications involving paper and cardboard. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global dyes and pigments market is expected to reach USD 31.2 billion by 2025, with basic dyes playing a crucial role in this growth due to their increasing use in various textile applications.
The application of basic dyes in textiles is favored for several reasons. Firstly, they exhibit excellent color fastness to light and provide bright, vivid shades, making them ideal for fashion and decorative textiles. Data from a recent industry survey indicates that the demand for vibrant, standout apparel has surged by over 15% in the last five years, driving the popularity of basic dyes. Additionally, basic dyes are praised for their compatibility with high-polymer synthetic fibers, thus enabling manufacturers to create innovative fabric blends that meet consumer demands for durability and aesthetic appeal.
Despite their benefits, the use of basic dyes also draws attention to the need for proper handling and application methods, as they may present challenges in terms of wash fastness when used on certain substrates. The adoption of advanced dyeing technologies and eco-friendly practices is being explored in the industry to enhance the performance of basic dyes while addressing environmental concerns. As the textile sector evolves, the versatility and effectiveness of basic dyes will continue to hold a pivotal position in shaping textile products and trends.
| Dye Type | Color Range | Applications | Properties | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Dyes | Vivid colors, typically neon | Cotton, acrylic, and other synthetic blends | High solubility, good brightness | Cost-effective and easy to apply |
| Acid Dyes | Wide range from pastels to dark tones | Wool, silk, nylon | Excellent lightfastness, good overall properties | Suitable for high-end textiles |
| Reactive Dyes | Bright and vivid hues | Cotton, cellulose fibers | Good washfastness, bright shades | Environmentally friendly options available |
| Disperse Dyes | Muted to bright colors | Polyester and other synthetic fabrics | Good heat stability, requires high temperature | Essential for dyeing synthetic textiles |
Basic dyes are characterized by their cationic nature, which allows them to easily bond with negatively charged substrates, making them suitable for a variety of applications in the textile industry. The chemical structure of basic dyes typically comprises aromatic amines or heterocyclic compounds, which include amino groups that enhance dye solubility and affinity for fibers. According to a recent industry report by Mordor Intelligence, the global market for basic dyes is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% from 2021 to 2026, driven by increasing demand in the textile sector.
The properties of basic dyes, including vivid color strength and good visibility, make them particularly advantageous for dyeing acrylic fibers, paper, and textiles. Their application is not limited to textiles but extends to areas such as specialized coatings and inks. A study published in the Journal of Textile Science & Engineering highlighted that basic dyes exhibit superior fastness properties in alkaline conditions, making them suitable for various environmental conditions encountered in textile processing. Understanding the chemical interactions and structural characteristics of these dyes is essential for optimizing their usage in different substrates, further emphasizing their importance in the textile industry.

Basic dyes play a significant role in the textile industry due to their vibrant colors and ease of application. They are particularly popular for dyeing fabrics like cotton, silk, and wool, primarily because of their compatibility with the chemical composition of these materials. According to the Textile Association, the market for basic dyes is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% through 2025, driven by their increasing application in the fashion and home textile sectors.
One of the most common applications of basic dyes in fabric dyeing is in creating bright and bold designs. These dyes are ideally used in techniques such as tie-dyeing, batik, and screen printing, enabling designers to achieve vivid prints that cater to contemporary trends. The ease of application allows for efficient production processes, which is particularly crucial in the fast-paced fashion industry. A recent industry report highlights that around 60% of dyeing operations for cotton textiles utilize basic dyes due to their ability to impart bright colors and their affordability compared to other dye types.
Furthermore, basic dyes are frequently employed in the production of active and sportswear where color retention and vibrancy are paramount. This segment of the textile market is evolving rapidly, with innovations aimed at enhancing the durability of colors under stress or exposure to washing. The Global Textile Dye Market report emphasizes that over 30% of textile manufacturers are opting for basic dyes in their activewear lines, recognizing the need for both aesthetic appeal and functional performance. This trend illustrates the importance of basic dyes in meeting consumer demands for high-quality, visually appealing textiles in an increasingly competitive market.

Basic dyes are widely used in textiles due to their vibrant colors and ease of application. They are particularly advantageous when dyeing acrylic fibers, as they readily bond to the surface of these materials, providing bright shades that attract consumers. According to a report by the International Journal of Clothing Science and Technology, approximately 40% of the world's synthetic fiber production is comprised of polyester and acrylic, indicating a significant market for basic dyes. Moreover, these dyes are soluble in water, which simplifies the dyeing process, allowing manufacturers to achieve a variety of color effects without complex procedures.
However, the use of basic dyes comes with certain limitations. One of the primary concerns is their poor wash and light fastness, which can lead to fading over time, particularly in high-wear garments. The American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists has reported that textiles dyed with basic dyes can have a wash fastness rating of only 2 to 3 on a scale where 5 represents the highest performance. This means that while basic dyes are suitable for certain applications, such as fashion items intended for short-term use or seasonal collections, they may not be ideal for products requiring high durability. Additionally, the environmental impact of basic dyes, particularly their non-biodegradable properties, raises concerns in an industry increasingly focused on sustainability.
The use of basic dyes in textiles has garnered attention not only for their vibrant colors but also for their environmental impact and safety considerations. Basic dyes are water-soluble dyes that provide bright hues and ease of application, making them popular in various industries. However, their environmental implications can be significant. The synthetic nature of these dyes often results in wastewater contamination, leading to severe ecological consequences if not treated properly before disposal. The presence of toxic substances in basic dyes can also threaten aquatic life and disrupt local ecosystems.
Safety considerations are paramount when handling basic dyes, as they can pose health risks to workers and consumers. Exposure to these dyes may result in skin irritation, respiratory issues, or other health concerns. Implementing proper safety protocols, such as the use of protective gear and adequate ventilation during the dyeing process, is essential to mitigate these risks. Moreover, adopting environmentally friendly practices, such as recycling wastewater and using non-toxic alternatives, can significantly reduce the ecological footprint associated with basic dye usage. By prioritizing safety and environmental sustainability, the textile industry can continue to enjoy the benefits of basic dyes while minimizing their negative impact.